What is a Modular Home?
An Introduction
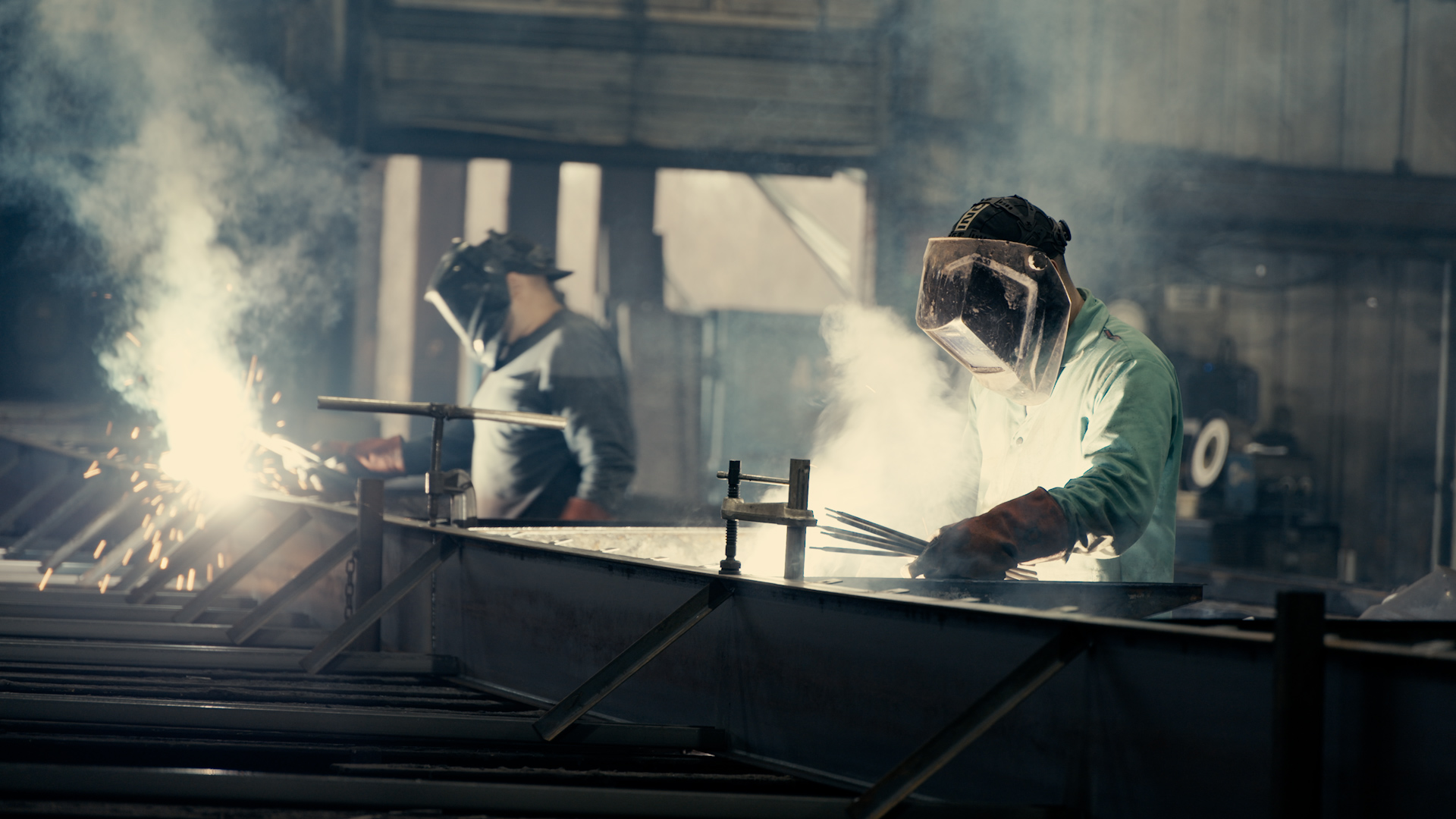
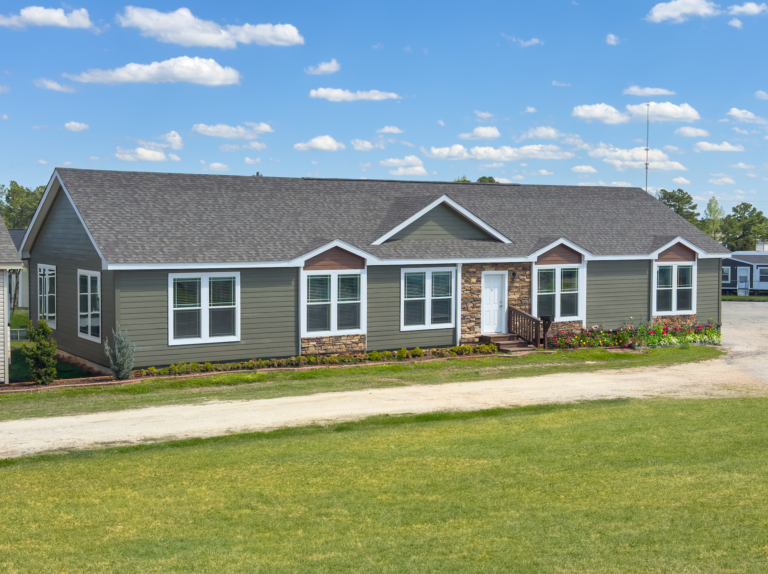
Modular homes have become an increasingly popular choice for homebuyers seeking cost-effective, high-quality, and energy-efficient housing solutions. Unlike traditional site-built homes, these homes are constructed in a controlled factory setting before being transported and assembled on-site. This method of construction offers numerous benefits, including reduced construction time, minimized material waste, and improved building quality.
The History
The concept of modular housing dates back to the early 20th century, when prefabrication techniques were introduced as a way to quickly build homes, especially during times of economic or housing crises. The Sears, Roebuck and Co. catalog homes, popular in the early 1900s, were an early form of prefabricated housing, though they were not modular by today’s standards.
During and after World War II, modular and prefabricated homes gained traction as a means to address housing shortages. By the 1950s and 1960s, advancements in factory construction and transportation allowed for the development of true modular housing, with pre-built sections assembled on permanent foundations. Over time, the modular home industry has evolved to include highly customizable and energy-efficient homes that can surpass traditional construction in both quality and durability.
The Definition
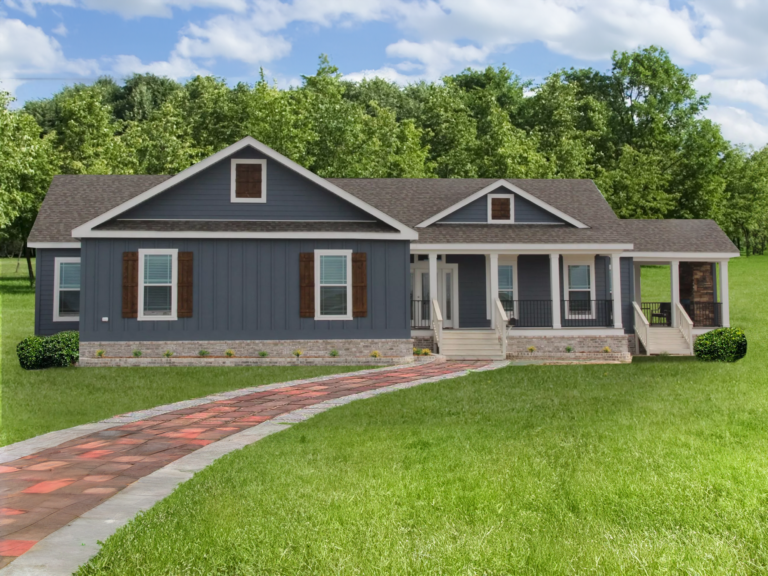
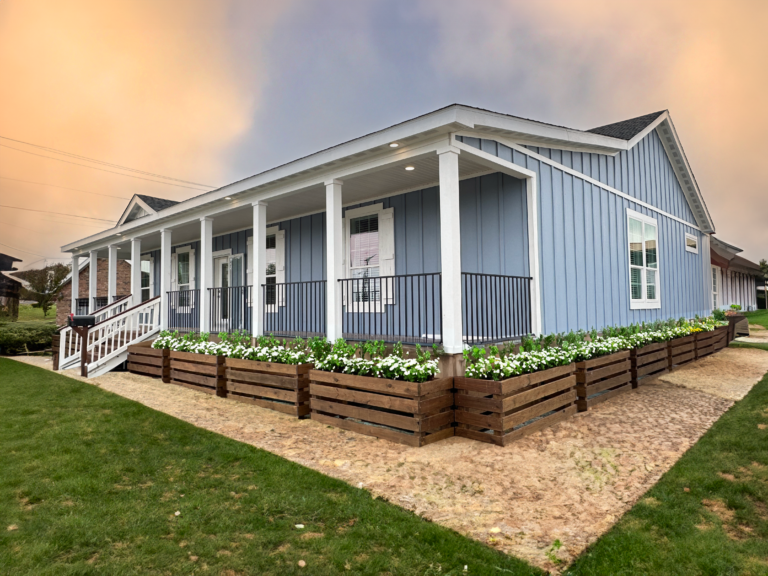
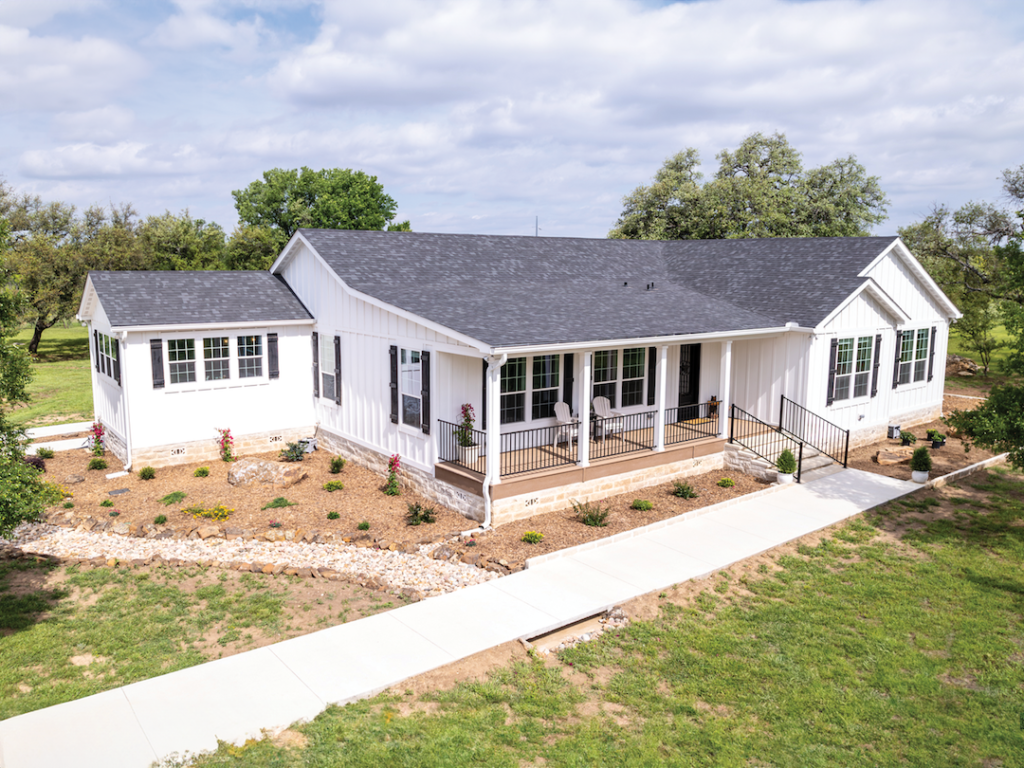
A modular home is a type of prefabricated home that is built in sections or modules in a factory and then transported to a permanent site for assembly. Unlike manufactured homes (also known as mobile homes), modular homes must meet local and state building codes, often surpassing codes for traditional site-built homes. Once assembled, these homes are indistinguishable from conventional houses in terms of appearance and functionality.

Modular Home vs. Other Types of Prefabricated Housing
To better understand these homes, it is essential to distinguish them from other forms of prefabricated housing:
1. Modular Homes: Built in factory-controlled sections and assembled on a permanent foundation. Must meet, or exceed, the same building codes as site-built homes.
2. Manufactured Homes: Built entirely in a factory and transported as a single unit or in sections. These homes adhere to the HUD (U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development) Code rather than local building codes.
3. Panelized Homes: Consist of factory-built wall panels that are assembled on-site. While similar to modular homes, they require more construction work at the final location.
4. Pre-cut Homes (Kit Homes): Homes where individual components are pre-measured and cut in a factory, then shipped to the site for assembly, often by the homeowner or contractor.
Key Terminology
To gain a comprehensive understanding of modular homes, it is important to be familiar with related terms:
– Modules: The individual sections of a modular home, built separately in a factory before assembly on-site.
– Factory-Built Housing: A broad term that encompasses modular, manufactured, panelized, and pre-cut homes.
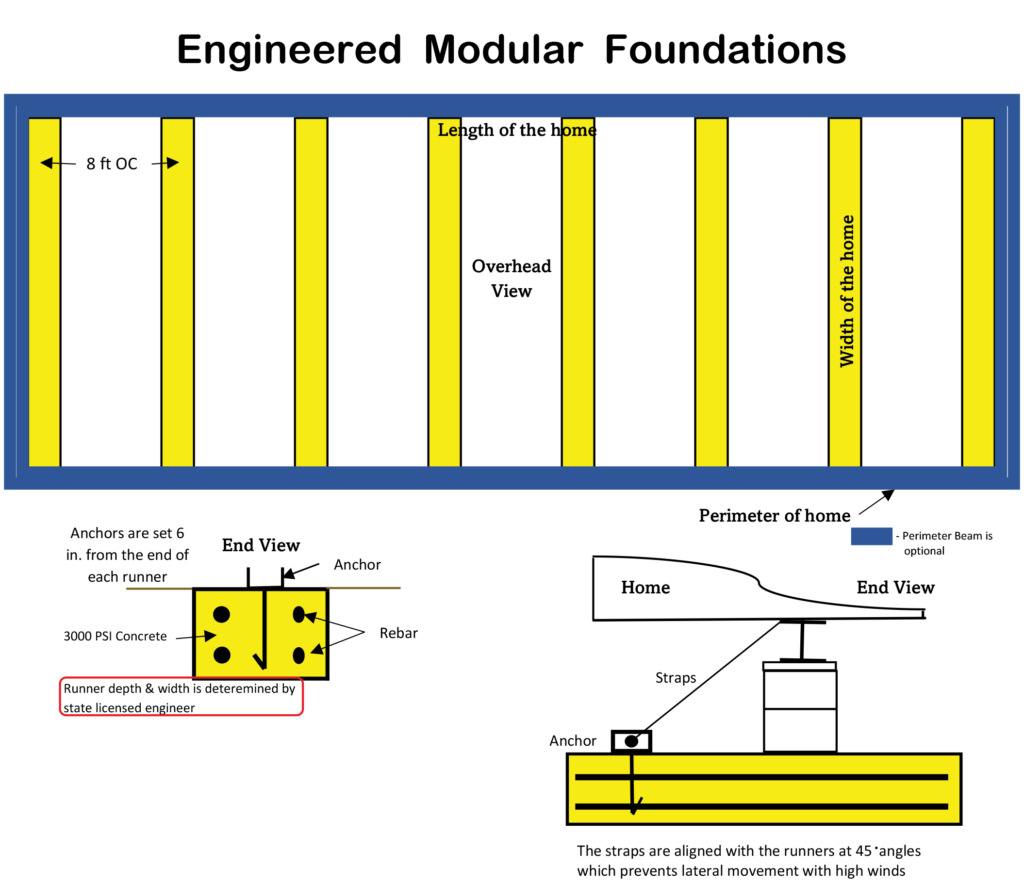
– Permanent Foundation: The base upon which the home is placed, ensuring it meets local zoning and construction regulations.
– Building Codes: Regulatory standards that dictate construction requirements. Modular homes must comply with local and state building codes.
– HUD Code: A set of federal guidelines that apply specifically to manufactured homes, not modular homes.
– On-Site Assembly: The process of putting together the pre-built modules at the final location.
– Customization: The ability to modify floor plans, finishes, and layouts to meet the homeowner’s preferences.
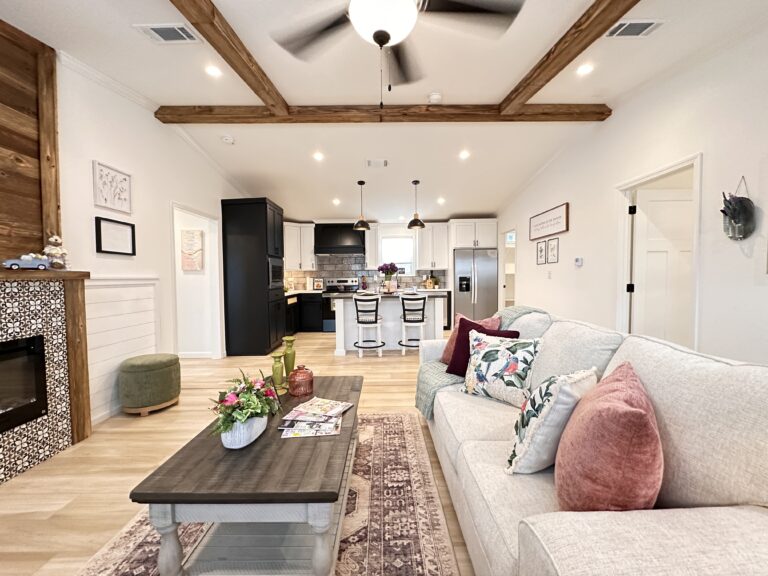
– Energy Efficiency: Many incorporate high-efficiency insulation, windows, and heating/cooling systems to reduce energy consumption.
Advantages of Modular Homes
They offer several advantages over traditional site-built homes:
– Faster Construction Time: Since modules are built indoors, weather delays are minimized, leading to quicker completion.
– Consistent Quality: Factory settings ensure precision and quality control throughout the building process.
– Cost Savings: Controlled construction reduces labor costs and material waste.
– Sustainability: Our homes use eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs.
– Customization: Buyers can personalize layouts, finishes, and designs to suit their needs.
– Durability: They are built to withstand transportation and on-site assembly, often making them sturdier than traditional homes.
Steps to Buying a Modular Home
Buying involves several important steps. Here’s what you need to know:
- Research and Planning: Decide on your budget, preferred home style, and location.
- Choose a Retailer/Builder: Compare modular home companies to find one that meets your needs and preferences.
- Select a Floor Plan: Work with the manufacturer to customize a layout that suits your lifestyle.
- Obtain Financing: Secure a construction loan or mortgage tailored to them.
- Site Preparation: Determine the needed land and improvements. Pratt Homes offers a complete turn-key solution.
- Factory Construction: Your home is built in modules under strict quality control.
- Transportation and Assembly: The modules are delivered and assembled on-site.
- Final Inspections and Move-In: Complete inspections, finish interior work, and move into your new home.
Common Misconceptions
There are several myths surrounding modular homes that can mislead potential buyers.
Here are some common misconceptions:
- They Are Mobile Homes: Unlike mobile homes, modular homes are placed on permanent foundations and must meet local building codes.
- Limited Customization: Modern modulars offer extensive design and customization options.
- Lower Quality: These homes are often built with higher precision and quality control than traditional site-built homes.
- Resale Value Concerns: Modular homes retain their value similarly to conventional homes, especially when well-maintained.
In Conclusion
Investing in a modular home can be an excellent decision for those looking for a high-quality, customizable, and energy-efficient living space. By understanding the buying process, advantages, and common misconceptions, you can make an informed decision that meets your housing needs. Whether you’re a first-time homebuyer or looking to upgrade, modular homes offer a practical and modern alternative to traditional home construction.